中国组织工程研究 ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (3): 416-420.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.03.016
• 纳米生物材料 nanobiomaterials • 上一篇 下一篇
含纳米SiO2或纳米TiO2微弧氧化纯镁生物涂层可促进成骨细胞增殖及活性
刘继光,王立峰,李慕勤,高 燕,王晓伟
- 佳木斯大学,黑龙江省高校生物医学材料重点实验室,黑龙江省佳木斯市 154007
Pure magnesium micro-arc oxidation coating containing nano-SiO2 or nano-TiO2 promotes proliferation and viability of osteoblasts
Liu Ji-guang, Wang Li-feng, Li Mu-qin, Gao Yan, Wang Xiao-wei
- Key Laboratory of Biomedical Materials in High Education of Heilongjiang Province, Jiamusi University, Jiamusi 154007, Heilongjiang Province, China
摘要:
背景:微弧氧化技术可增强镁及其合金的耐腐蚀性,提高其表面生物性能。
目的:为了调控医用纯镁的生物活性,在镀液中添加纳米SiO2或纳米TiO2对纯镁微弧氧化涂层改良,研究其对成骨细胞增殖及分化的影响。
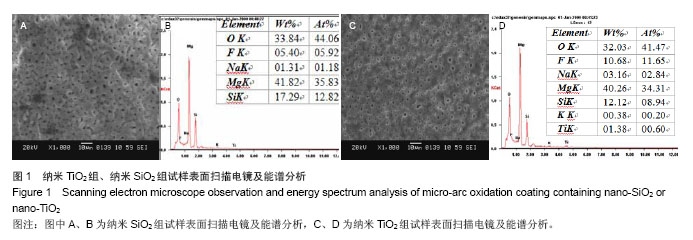
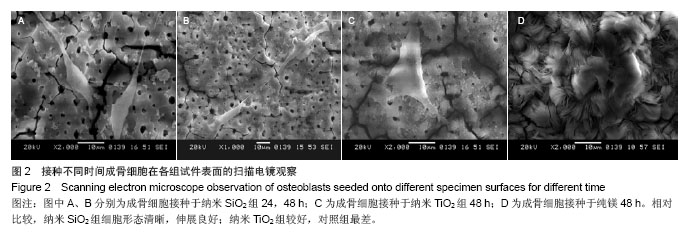
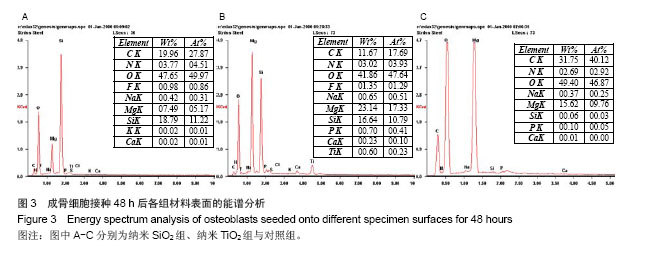
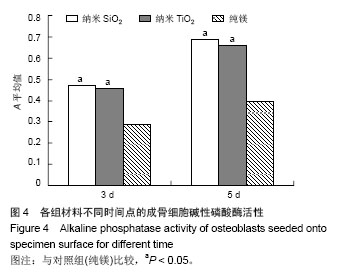
方法:将圆形镁片分为3组,其中两组分别置入含7.5 g/L纳米SiO2或4.8 g/L纳米TiO2的硅酸盐电解液中进行表面微弧氧化处理,以未作任何处理的纯镁作为对照。将第3代成骨细胞分别接种于3组试件表面,观察成骨细胞的早期形态、增殖与碱性磷酸酶活性。
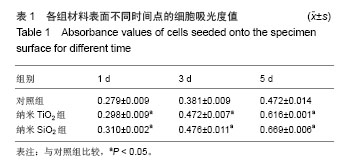
结果与结论:成骨细胞在纳米SiO2组、纳米TiO2组试件表面生长状态良好,轮廓清晰,呈长梭形,多角形;在对照组表面生长状态较差。CCK-8检测显示,3组细胞吸光度值与碱性磷酸酶活性随时间推移呈上升趋势,纳米SiO2组、纳米TiO2组试件接种1,3,5 d的细胞增殖活性高于对照组;纳米SiO2组、纳米TiO2组接种3,5 d的细胞碱性磷酸酶活性高于对照组。结果表明纳米SiO2或纳米TiO2微弧氧化生物涂层可促进成骨细胞增殖及成骨活性,具有良好的生物相容性。
中图分类号: